Breast cancer is a disease that starts with a malignant tumor in the breast. A malignant tumor is a mass of cells that gets out of control. Cancer cells can also metastasize, or move to other tissues or parts of the body.
Cancer can develop in any of three types of breast tissue: labial, ductal and connective tissue.
Most cancers start in the lymph nodes, or ducts, along with the milk to the nipple. (1) But fibrous and fatty connective tissue can also develop tumors that surround the labules and ducts.
There are many different types of breast cancer. Determine the type of breast cancer and its stage, or how far it has progressed, and how to treat it.
Breast cancer that spreads to normal tissue is called breast cancer. Non-vascular breast cancer resides inside the breast labia or duct. (2)
Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer
If you experience any of the following symptoms, check with your healthcare provider. (3.4)
A lump inside or near the breast
Warm or indistinct tenderness in the breast
A hard, thick or swollen area in the chest
Nipple tenderness without any other reason
Nipple discharge (other than breast milk) especially clear or bloody discharge
An indistinct change in the color, texture, size, or shape of the breasts or nipples
Sliding or growing holes on the breast (such as orange peel)
Chest, redness, scratching or general pain in the breasts or nipples
Nipples that turn inward without explanation
Irritable or itchy breasts
Itching in breast cancer, which can be a sign of inflammatory breast cancer
Although a lump may be a sign of cancer, about 80 to 80 percent of breast lumps are not serious. (5) The most common causes of nonsensical tumors include:
Fibrostic changes as a result of hormonal fluctuations
Cysts
A benign tumor called a fibrodynomas
Wound-like growth is called intracellular papillomas
Fat tissue that results from breast trauma
Causes and Risk Factors of Breast Cancer
The biggest risk factors for this disease, in addition to women’s gender, include:
Age – The risk begins to increase after the age of 50
A family history
Genetics
Previous radiation exposure
Every woman’s risk involves a combination of different factors. If you are worried, your doctor can help you assess how high your risk is, and whether you need to take any additional precautions regarding screening. (6)
Genetic testing for breast cancer: BRCA1 and BRCA2
In some cases, especially if you have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, your doctor may recommend genetic testing for two common genetic mutations that increase the risk of developing these two cancers. : BRCA1 and BRCA2. Hereditary BRCA gene mutations cause about 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers and about 10 to 15 percent of ovarian cancers. (7)
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed?
Using a mammogram, doctors can screen for breast cancer. A mammogram is an X-ray that contains a small amount of radiation that allows doctors to detect abnormalities in the breast tissue.
Breast cancer can also be diagnosed with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, or 3D mammography (called breast tomocentesis).
An MRI uses a large magnet to take pictures of the breast. An ultrasound sends sound waves to the breast that produce an image when it returns. A 3D mammogram uses an X-ray like a regular mammogram, but it takes several slices of the breast at different angles to create a 3D image. (8)
Screening tests look for possible symptoms of breast cancer but cannot diagnose it. If doctors notice a suspicious tumor or an abundance of cells, they can use some of these similar tests to get a closer look at the abnormal area. A diagnostic mammogram provides more detail on the breast image. (9)
The only way to make a specific diagnosis of breast cancer is a biopsy. A biopsy involves removing some breast tissue or fluid from a suspicious area and looking at the cells under a microscope. (10)
Finding the best team for treatment
Once you have been diagnosed, you will have to make a number of decisions about the healthcare providers who will handle your treatment.
Cancer treatment usually involves a team of people, such as a surgeon, medical oncologist, nurse practitioner, a counselor, patient navigator, and specialists related to your type of cancer.
The factors to consider in choosing your oncologist and treatment team are your type of cancer, what your insurance will cover, travel by appointments and procedures, and their expertise in your qualifications and recommendations for others.
Even after you have a treatment team, it’s a good idea to find another specialist to get a second opinion on your diagnosis and treatment options. It is always acceptable and normal to change doctors during your treatment if you need to.
Breast Cancer Stages
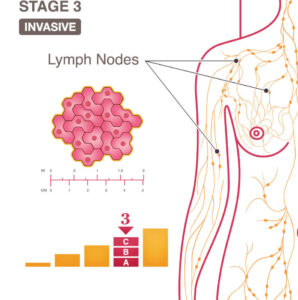
Doctors use the stages of breast cancer to tell how far the cancer has spread or spread. Stages 0 to 4 (often expressed in Roman numerals, I – IV). Each phase has subcategories of A, B or C. (11)
Stage 0 cancer is unnecessary and shows no evidence of leaving the part of the breast where it started. One type of stage 0 cancer cytoskeleton (DCIS) is ductal carcinoma.
Stage 1 Cancer cells are spreading around the breast tissue, but the group of cancer cells or tumors is very small. It is usually easily treated.
Stage 2 cancer is on the rise but only lives in the breast or nearby lymph nodes. Treatment is usually not very difficult.
Stage 3 cancer has begun to invade the lymph nodes, muscles, and other body tissues near the breast, but has not spread to other organs. Treatment depends on the individual and type of breast cancer.
Stage 4 cancer is highly developed and has spread to many organs or other parts of the body. Stage 4 Breast cancer is considered incurable, but women can live many years or more with ongoing treatment.